What is Leverage in Forex Trading Market?
Leverage in Forex is effectively just a short-term, Conceptual
loan.
It is Conceptual in the sense that you don’t physically receive a loan – it’s simply an
automatic credit line Widen by your broker in respect of your forex
trades.
This will normally be Contain of a degree of security money, known as
margin, which usually accounts for a certain ratio of the trade, with the
remainder being comprised of leverage funding.
More About Leverage in Forex: As you are thinking about, how a small
investor can trade such large amounts of money.
Think of your broker as a bank who basically fronts you $100,000 to buy
currencies.
All the bank asks from you is that you give it $1,000 as a trusted
deposit, which he will hold for you but not necessarily keep. Sounds too
good to be true? This is how forex trading using leverage works.
The amount of leverage you use will depend on your broker and what you
feel comfortable with.
Typically the broker will require a trade deposit, also known as "account margin" or "initial
margin."
Once you have deposited your money you will then be able to trade. The
broker will also specify how much they require per position (lot) traded.
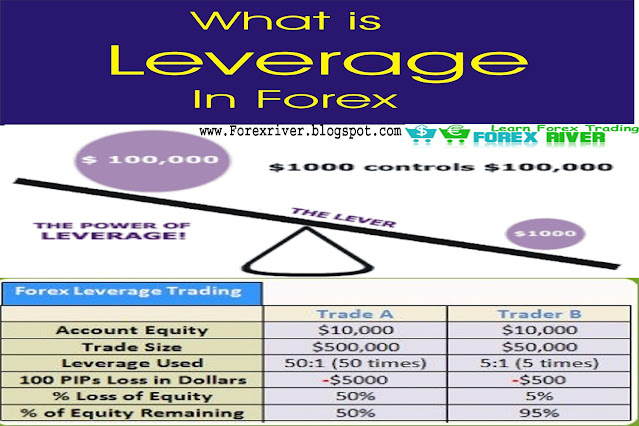
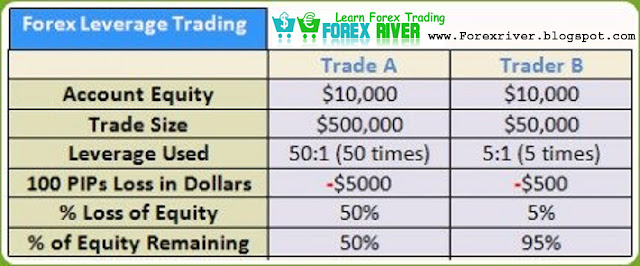
For example, if the allowed leverage is 100:1 (or 1% of position
required), and you wanted to trade a position worth $100,000, but you only
have $5,000 in your account. No problem as your broker would set aside
$1,000 as down payment, or the "margin," and let you "borrow" the rest. Of course, any losses or gains will be
deducted or added to the remaining cash balance in your account.
The minimum
security (margin)
for each lot will vary from broker to broker. In the example above, the
broker required a one percent
margin. This means that for every $100,000 traded, the broker wants $1,000 as a
deposit on the position.
What is the best leverage to use in forex?
leverage of 1:100 in Forex is the best leverage to be used in forex
trading. Leverage of 1:100 means that with $500 in the account, the
trader has $50,000 of credit funds provided by the broker to open
trades.
Most forex brokers allow a very high leverage ratio, or, to put it
differently, have very low
margin requirements. This is why profits and losses change high in forex trading
even though currency prices do not change all that much — certainly not like
stocks. Stocks can double or triple in price, or fall to zero; currency
never does. Because currency prices do not change Significantly, much lower
margin requirements are less risky than it would be for stocks.
Note, however, that there is Sizeable risk in forex trading, so you may be
point to
margin calls when currency exchange rates change Quickly.
How Does Leverage Work in Forex Trading?
With 100:1 leverage a trader can open a position 100 times greater than
they could without leverage.
For example:
If the cost to purchase .01 lots of EUR/USD is normally $1000 and the
broker offers 100:1 leverage, then the trader must put up only $10 as
margin. Of course, the trader can use as little leverage as they want.
Why is leverage dangerous?-Risk in Leverage in Forex Trading
Higher leverage means higher risk. Most professionals use a very low
leverage ratio, or none at all, and a modest risk percentage per trade.e.g.
a trade that can be entered using $1,000 of trading capital, but has the
potential to lose $10,000 of trading capital).
Leverage and Margin Calculator in Forex Trading Market:
How to Use the Forex Margin Calculator?
Currency pair: In this field traders can select from several Major
Forex crosses, some Minor pairs, from the most popular cryptocurrencies
versus the USD (BTC, ETH, LTC, Stellar and Ripple), and Gold/Silver versus
the USD. For our example, let's choose the EUR/USD.
Deposit currency: Margin values are different for each Forex pair,
or any other financial instrument, and subject to its current market quote.
By selecting the deposit currency, it will be possible to accurately display
the margin amount of the selected instrument in the trader's account base
currency (from AUD to ZAR). We will choose GBP as our deposit currency, for
this example.
Leverage: In this field traders just need to input their current
leverage, offered by their broker, or they can choose from a range of 1:1
to a maximum of 600:1 to simulate the amount of margin used to open a
position with different leverage options. For our example, we will select
a leverage of 30:1.
Lots (trade size): Simply type in the lot size. Remember, one
standard lot of a Forex pair is 100,000 units per 1 lot, but units per 1
lot vary for the non-forex pairs. In this field there's also the option of
switching between lots or units for the calculations. For our example, we
will use a trade size of 0.10.
Next, we click the "Calculate" button.
The results: Using all the formulas illustrated above, and the data
supplied, the Forex Margin Calculator tell us that to open a trade
position, long or short, of a 0.10 lot EUR/USD, with a 30:1 leverage
trading account, and with the current EUR/GBP exchange rate of 0.90367, we
would need a margin of £ 301.22.
The Forex Margin Calculator can also be used to find the least "expensive"
pairs to trade. For the same example above, and by using the same
calculating parameters (30:1 leverage and a 0.10 lot trading position), if
instead of selecting the EUR/USD we choose the AUD/USD, then we see that
the margin required would be much less, only 186.89 GBP.





No Comments